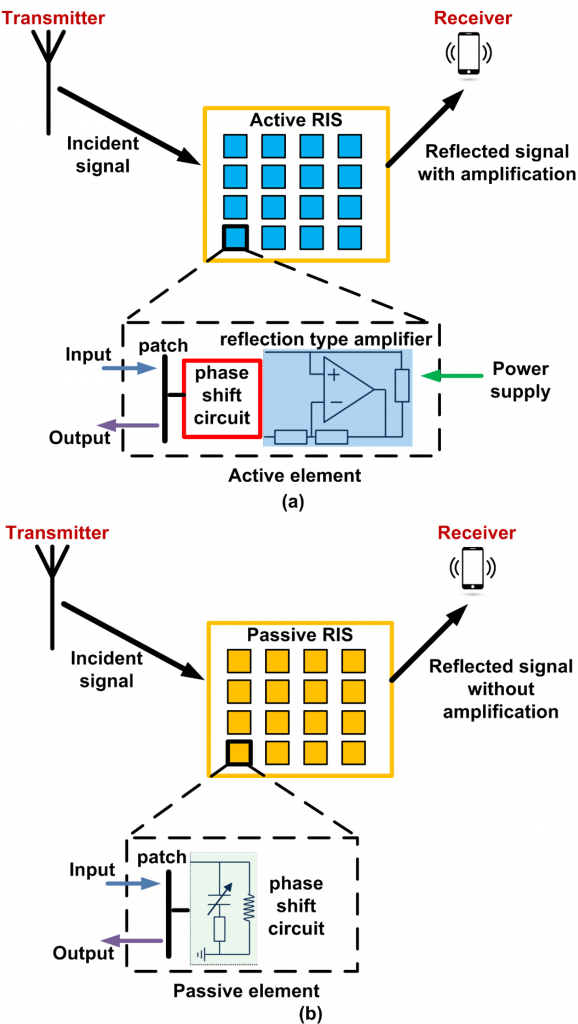
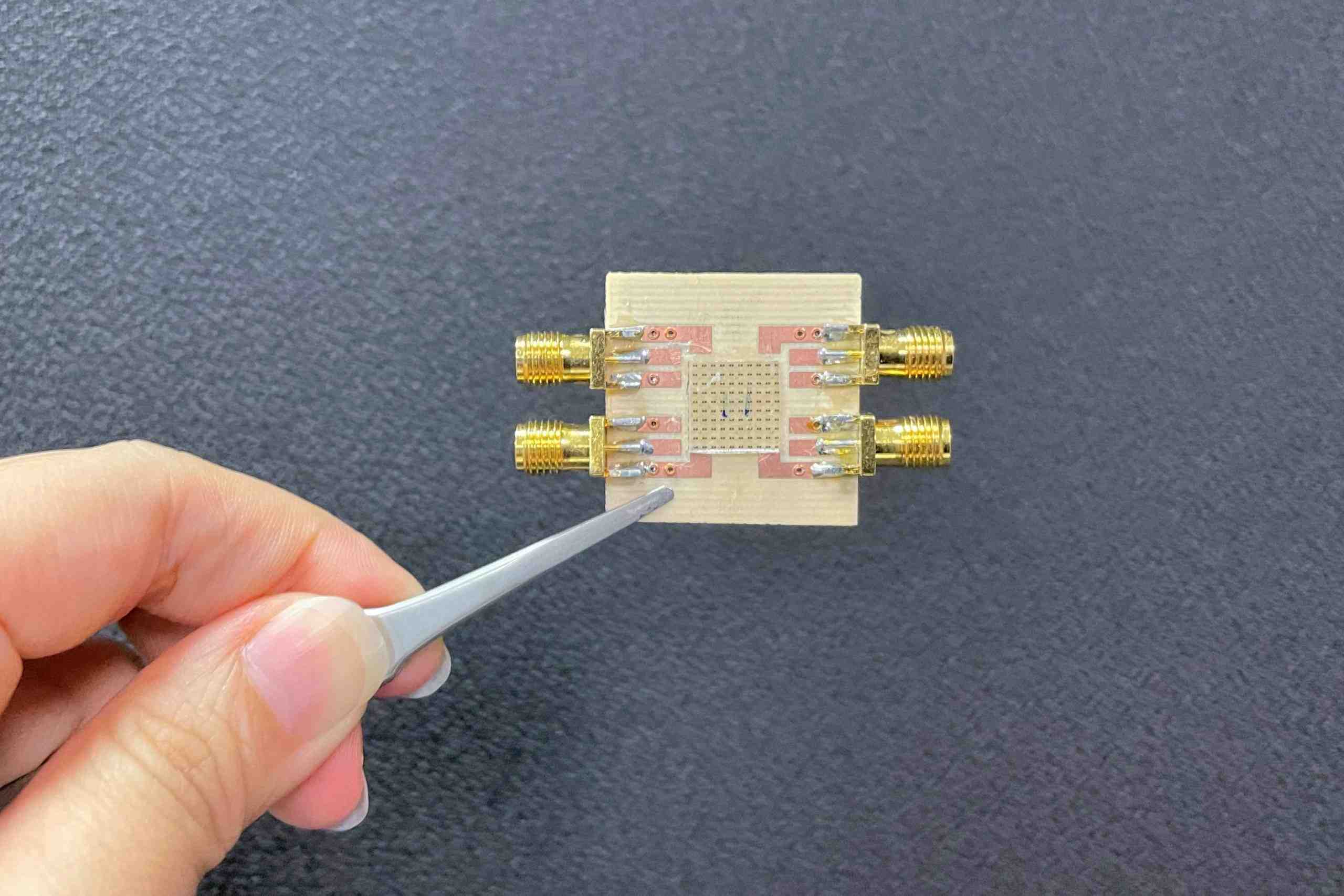
Researchers have developed a new metasurface-based antenna, which represents an important step in making it convenient to collect energy from radio waves, such as those in cellular networks or Bluetooth connections. This technology could potentially offer wireless power to sensors, LEDs and other simple devices with low power requirements.
“By eliminating cable connections and batteries, these antennas can help reduce costs, improve reliability, and make some electrical systems more efficient,” said research team leader Jiangfeng Zhou of the University of South Florida. “This would be useful for smart home sensors such as those used for temperature, lighting and motion or sensors used to monitor the structure of buildings or bridges where replacement of a battery is difficult or impossible.”
In the Journal of Optical Materials Express, the researchers report that laboratory tests of their new antenna have shown that it can produce 100 microwatts of power, enough to easily power low-power radio waves. This was possible because the metamaterial used to make the antenna shows perfect absorption of radio waves and was designed to work with low intensities.
“Although more work is needed to miniaturize the antenna, our device overrides a key threshold of 100 microwatts of the collected power with high efficiency using ambient power levels found in the real world,” said Clayton Fowler, team member who manufactured and assembled the sample. the measurements. “The technology could also be adapted so that a radio wave source could be supplied for electricity or appliances around a room.”
Scientists have been trying to capture the energy of radio waves for a long time, but it was difficult to get enough energy to be useful. This is changing thanks to the development of metamaterials and the ever-increasing number of ambient sources of radio frequency energy available, such as cellular networks, Wi-Fi, GPS, and Bluetooth signals.
“With the huge explosion in radio wave-based technologies, there will be a lot of waste electromagnetic emissions that are collected,” Zhou said. “This, combined with advances in metamaterials, has created a mature environment for new devices and applications that can benefit from collecting and using this waste energy.”
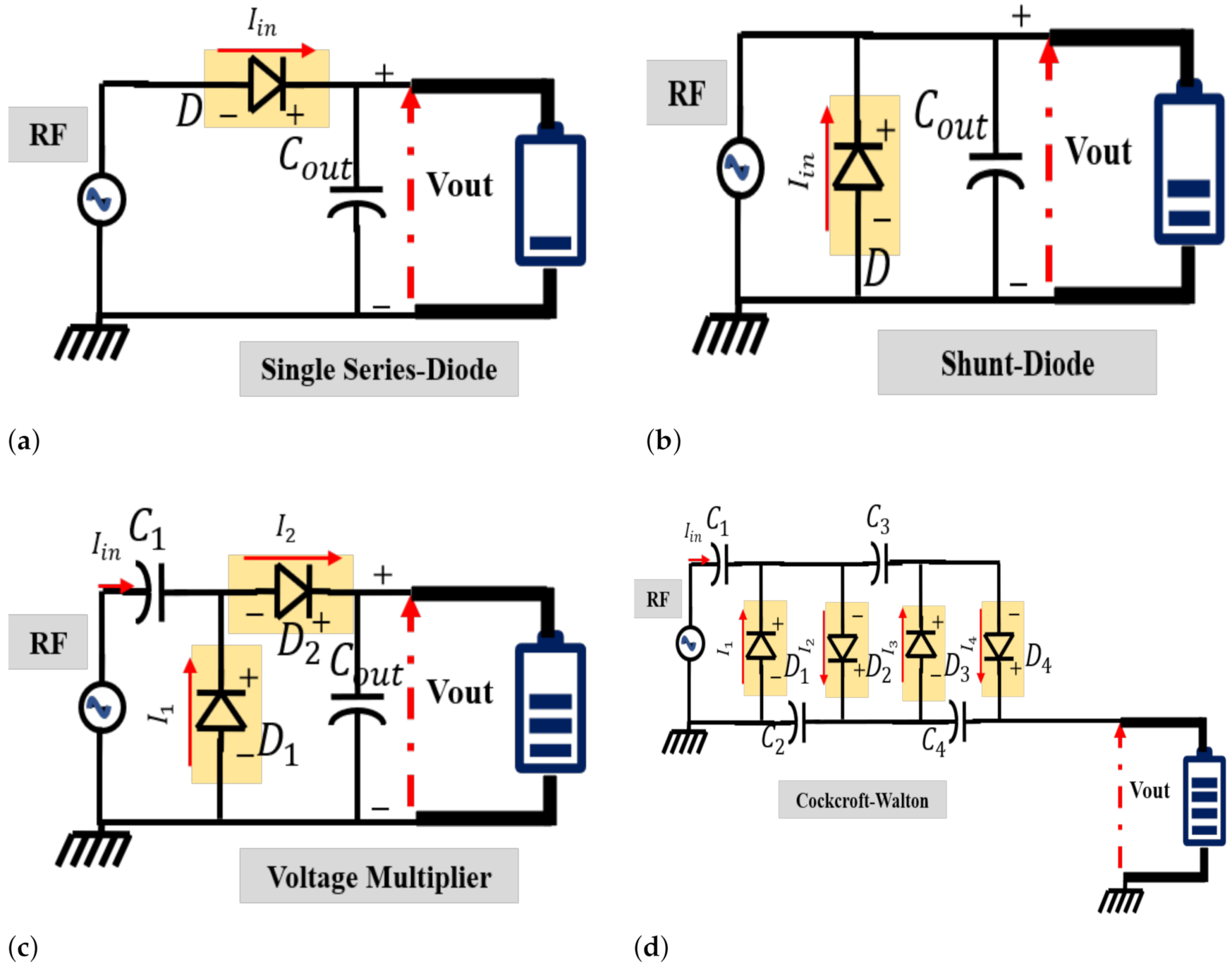
Metamaterials use small, carefully designed structures to interact with light and radio waves in ways that natural materials do not. To make the energy harvesting antenna, the researchers used a metamaterial to design a high absorption of radio waves and this allows a higher voltage to fly over the diode of the device. This has improved its efficiency to power radio waves and power, especially at low intensities.
Testing with ambient power levels
For laboratory tests of the device, which measured 16 cm by 16 cm, the researchers measured the amount of force while changing the power and frequency of a radio source between 0.7 and 2.0 GHz. They have proven the ability to collect 100 microwatts of power from radio waves with an intensity of only 0.4 microwatts per centimeter square, approximately the level of the intensity of the radio waves 100 meters from a cell phone tower.
“We also placed a cell phone very close to the antenna during a phone call, and it collected enough power to start an LED during the call,” Zhou said. “While it would be more convenient to collect energy from cell phone towers, this has proven the power capabilities of the antenna.”
Because the current version of the antenna is much larger than most of the devices that would potentially make it, researchers are working to make it smaller. They also want to make a version that could collect energy from different types of radio waves simultaneously so that more energy could be collected.
Material provided by Optica. Note: Content can be changed for style and length.
How is a radio wave created?
Contents
- 1 How is a radio wave created?
- 2 Are semiconductors used in radios?
- 3 How do radios use radio waves?
- 4 How does a FM transmitter work?
- 5 Did old radios need electricity?
- 6 How do you harness electromagnetic waves?
Radio waves are generated by charged particles that undergo acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the black body radiation emitted by all hot objects.
How are GCSE radio waves made? Radio waves are produced when alternating current flows in an antenna. It spreads and travels through the atmosphere. To see also : Organic semiconductors come to the 5G circuit. Another antenna is used as a detector. The radio waves produce alternating current in it, at a frequency corresponding to that of the waves.
How can we make radio waves at home?
When a direct electric current is applied to a wire, the current builds an electromagnetic field around the wire. This field sends a wave to the outside of the wire. This may interest you : RF Plasma Generator Market To Reach US$ 5.1 Billion By 2031, TMR. When the current is removed, the field collapses, sending a wave again.
How can we make electromagnetic waves at home?
What household items use radio waves?
Just like your current meter uses RF communication, so do everyday devices such as radios, cell phones, baby monitors, and wireless networks.
What can cause radio waves?
Radio waves can be generated by natural sources such as lightning or astronomical phenomena; or through artificial sources such as broadcast radio towers, cell phones, satellites and radar. On the same subject : Global Radio Frequency Transceiver Chip Market (2022 to 2028) – Business Strategies Broadcom Corporation, GCT Semiconductor, Intel, Ericsson – The Bite.
Can humans affect radio waves?
Some people may have significant RF exposure as part of their job. This includes people who receive antenna towers that emit communication signals and people who use or maintain radar equipment.
What can affect radio waves?
As a form of electromagnetic radiation, such as light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering.
Are semiconductors used in radios?
Two common semiconductor materials are germanium and silicon, to which small quantities of toxins such as indium, gallium, arsenic or phosphorus are added to give them electrical charges.
What are radio receivers made of? In modern receivers, quartz crystal, ceramic resonator or surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters are often used, which have sharper selectivity compared to networks of capacitor-inductor tuned circuits. Tuning: To select a specific station, the radio is “tuned” to the frequency of the desired station.
What type of circuit is used in a radio?
The combination of C1 and L1 includes a resonant circuit, referred to as a tank circuit. Its purpose is to select one from many available radio signals. The variable capacitor C1 allows you to tune to different signals. The diode passes the positive half cycles of the RF, deletes the negative half cycles (c).
How do you make a radio circuit?
What type of circuit is a radio?
Radios consist of many specialized electronic circuits designed to perform specific tasks – Radio Frequency Amplifier, Mixer, Variable Frequency Oscillator, Medium Frequency Amplifier, Detector, and Audio Amplifier. The radio frequency amplifier is designed to amplify the signal of a radio transmitter transmitter.
How does a radio circuit work?
A radio receiver is the opposite of a radio transmitter. It uses an antenna to pick up radio waves, processes these waves to extract only those waves that vibrate at the desired frequency, extracts the audio signals attached to these waves, amplifies the audio signals, and finally plays them on a speaker.
How do radios change frequencies?
There are two ways radio stations modulate their carrier waves: amplitude modulation, or AM, and frequency modulation, FM. AM radio transmits a carrier wave that maintains a constant frequency, while the superimposed sound wave modulates its amplitude.
How do you make a radio circuit?
How does a transistor work in a radio?
The function of transistors and radios is simple. Sounds are picked up by a microphone and converted into electrical signals. These signals travel through a circuit, and the transistor amplifies the signal, which is then much louder when it reaches a speaker.
Are transistors still used in radios?
Transistor radios are still commonly used as car radios. Billions of transistor radios are estimated to have been sold worldwide between the 1950s and 2012. The pocket size of transistor radios has triggered a change in popular music listening habits, allowing people to listen to music wherever they go.
How does the transistor work?
A transistor works when the electrons and holes are trapped across the two junctions between n-type and p-type silicon. The small current that we turn off at the base creates a large current between the emitter and the collector.
How do radios use radio waves?
You can tune a radio to a specific wavelength or frequency and listen to your favorite music. The radio & quot; receives & quot; these electromagnetic radio waves and convert them into mechanical vibrations in the speaker to create the sound waves you hear.
How do radio waves work? A radio wave is generated by a transmitter and then detected by a receiver. An antenna allows a radio transmitter to send energy into space and a receiver to receive energy from space. Transmitters and receivers are typically designed to operate over a limited range of frequencies.
What are 3 things that use radio waves?
Radio waves are widely used in modern technology for fixed and mobile radio communications, emissions, radar and radio navigation systems, communications satellites, wireless computer networks and many other applications.
What household items use radio waves?
Just like your current meter uses RF communication, so do everyday devices such as radios, cell phones, baby monitors, and wireless networks.
What are example of radio waves?
AM and FM Radio Broadcasting which transmit the sound to a wide audience. Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to obtain information about objects. Bluetooth and wireless communication use radio waves to create connections between devices.
Do radios pick up radio waves?
Unless you are sitting right next to the transmitter, your radio receiver will need an antenna to help pick up the transmitter’s radio waves from the air.
What device picks up radio waves?
A radio communication is a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a cable, or simply a radio, an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information from them into a usable form.
Can radios send signals?
Modern digital radio conveys information as a digital signal, encoded in the form of numbers. Millions of radio waves – which carry sound wave signals and digital signals – reach your receiver every second. The tuner of the receiver selects a specific signal. Its amplifier amplifies that signal.
How radio waves are used for radio and television broadcasts?
In radio transmissions, sounds and radio waves are encoded, and then the waves are sent through the atmosphere of a radio tower. A radio receiver recognizes the waves and changes them back to sounds. You may have listened to both AM and FM radio stations.
How are radio waves used to encode sounds and images in television broadcasts?
For TV broadcasts, sounds are coded with frequency modulation, and images are coded with amplitude modulation. The coded waves are transmitted by a television tower. When waves are picked up by television sets, they are decoded and changed back to sounds and images.
How are radio waves used in television?
Radio waves do more than just bring music to your radio. They also carry signals for your TV and cell phones. The antennas on your TV receive the signal, in the form of electromagnetic waves, emitted by the TV transmitter. It is displayed on your TV screen.
How does a FM transmitter work?
FM transmitters work with a converter that transforms the audio output of an existing source, such as your car stereo, into analog audio signals. The signals are then converted to FM signals so that motorists change their radio frequency of the vehicle to suit the transmitter.
How do Bluetooth FM transmitters work in cars? What is this? A Bluetooth FM transmitter uses the low power, short-term frequency to send and receive information with radio waves. If your phone is paired with the car kit and it allows you to automatically use desired features, in this case the music.
Does FM transmitter work without radio?
It will have no effect on the strength of your FM signal. It only uses the FM band to transmit sound to your car radio. Since it will be only a few meters from your antenna, you should not experience any interference. In fact, being further away from current radio broadcasts makes it better to work.
Will FM transmitter work with no signal?
If your car does not receive a signal from a normal radio transmitter, an FM transmitter will not be recorded either.
How do I use a just wireless FM transmitter?
To use, simply plug the FM transmitter into the 12V power port of your vehicle or car cigarette lighter, tune the radio in your car to the same frequency as the FM transmitter, and start listening!
- Go to your orders and start the return.
- Select the return method.
- Send it!
Are FM transmitters illegal?
Part 15 certified FM transmitters can be used legally by anyone, anywhere in the United States without the need for a license.
Are low power FM transmitters legal?
Regardless of popular misconceptions, it is not legal to broadcast on low power FM, or on any power, without an FCC license. It does not matter if you are less than 100 watts or less than 1 watt.
What is the maximum distance an FM transmitter can broadcast without a license?
What is the maximum distance that an unlicensed FM transmitter can transmit? The fast response is about 200 feet for an FM transmitter covered under Part 15 (Read FCC Public Note of July 24, 1991).
How does a simple FM transmitter work?
Generally, the FM transmitter uses VHF radio frequencies from 87.5 to 108.0 MHz to transmit and receive the FM signal. This transmitter reaches the excellent range with less power. The performance and operation of the wireless audio transmitter circuit depends on the induction coil & variable capacitor.
How can I make a simple FM transmitter?
How does a simple transmitter work?
Radio works by transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves. The radio signal is an electronic current that moves back and forth very quickly. A transmitter radiates this field outward through an antenna; a receiver then picks up the field and translates it to the sounds heard over the radio.
Did old radios need electricity?
Radios that did not use mains power were the original types because radios used direct power, but the home supply was usually alternating power. While it was possible to produce direct current from alternating current, the necessary equipment could cost more than the rest of the radio.
Can a radio without power work? But along with mobile and social media alarms, the humble 100-year-old technology of radio has once again proved its worth. It is reliable when everything else – the electrical network, internet, cell service – is down. Radio can transmit information instantly when it has backup power.
How did an old radio work?
Filaments were driven with 6V and later 12V DC power from the electrical system of the vehicle directly. With the introduction of transistors, formerly only suitable for audio frequencies, car radios were valve sets with a transistor output stage; Manufacturers have promoted them as transistor sets.
How were the first radios powered?
In 1922, regular wireless broadcasts for entertainment began in the UK from the Marconi Research Center 2MT in Writtle near Chelmsford, England. Earlier radios had the full power of the transmitter run through a carbon microphone.
How did a radio work?
Radio works by transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves. The radio signal is an electronic current that moves back and forth very quickly. A transmitter radiates this field outward through an antenna; a receiver then picks up the field and translates it to the sounds heard over the radio.
Did old radios use batteries?
All early radios used batteries – as many as three batteries in the earliest sets. These batteries were known as A, B, and C. Radio engineers designed to quickly eliminate circuits using the C battery in a typical radio circuit. That left two battery supplies, A and B.
Does a radio have a battery?
Most two-way radios come with rechargeable batteries that can be recharged, used, and recharged many times before they are exhausted. There are many factors that influence how long a two-way battery will last. On average, a two-way radio battery lasts between 18 and 24 months.
When did radios have batteries?
If you’ve followed my series of articles, you already know that the earliest radios were powered by batteries. In the mid-1930s, newer tube technology and more efficient batteries enabled portable, relatively lightweight battery radios.
Do old radios need electricity?
No! Many radio receiver designs exist that use no power other than the energy of the EM waves (radio signal) itself! Note that radio signals themselves are alternating current.
Do radios use electricity?
In general, the average radio uses 1 – 3 kWh of electricity. However, if you want to be more secure, you can check the power rating of your radio (either on the radio itself, or a label found on the cable, or in the manual) that gives you an indication of its maximum power consumption.
Can radios work without electricity?
Crystal radio receivers are a very simple type of battery-free radio receiver. They do not need a battery or power source other than the power they receive from radio waves with their long outdoor wire antenna.
How do you harness electromagnetic waves?
Can you use energy from radio waves? An international team of researchers has developed a way to collect energy from radio waves on portable devices. From microwave ovens to Wi-Fi connections, the radio waves that permeate the environment are not only signals of the energy consumed, but are also energy source itself.
Can you harness electromagnetic waves?
Terahertz waves are pervasive in our daily lives, and when used, their concentrated power could potentially serve as an alternative energy source. However, to date, there has been no practical way to capture and convert them into a usable form.
Can electromagnetic waves be used as a weapon?
Electromagnetic weapons are a type of directed energy weapon that uses electromagnetic radiation to deliver heat, mechanical or electrical energy to a target to cause pain or permanent damage. They can be widely used against humans, electronic equipment and military targets, depending on the technology.
Can we amplify electromagnetic waves?
Results of the calculation show that, in regions far from the resonance, electromagnetic waves can still be amplified over a wide frequency range, forming plateaus below each resonant peak. As the harmonic wave number increases, the peak value of the growth rate decreases and the width of the peak decreases as well.
Can we control electromagnetic waves?
Metamaterials are artificial structures consisting of subwavelength unit cells to control electromagnetic (EM) waves. The spatial coding representation of metamaterial has the ability to describe the material in a digital way.
Can electromagnetic waves be controlled?
By properly designing and arranging the metasurface elements to form an array, the singularity of the metasurface on the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave beam can be controlled; such unique electromagnetic properties offer additional opportunities to innovate new antennas.
Can you slow down electromagnetic waves?
The electromagnetic spectrum is a spectrum of different frequencies. These frequencies can all travel at the same speed in a vacuum, but materials slow them down and can affect different frequencies differently.