This article is part of the TechXchange: Diving into EMI, EMC and Noise
Members can download this article in PDF format.
Suppressing RF EMI requires multiple solutions that designers can implement on their board design or with shielding materials. Good electromagnetic shielding helps minimize or even block electromagnetic interference (EMI) to the best creative RF electronic design from a circuit designer.
This article presents techniques to effectively apply EMI shielding and filtering. It not only ensures smooth operation of the electronic design, but also accelerates the time-to-market.
Where Does Typical RF EMI Come From?
Contents
- 1 Where Does Typical RF EMI Come From?
- 2 Electromagnetic Shielding
- 3 Electrostatic Shielding
- 4 EMI Filtering for RF Designs
- 5 Summary
- 6 References
- 7 Does foil block EMI?
- 8 Can copper block magnetic fields?
- 9 How do you use EMI shielding tape?
- 10 Is shielding an effect?
- 11 What is EMI shielding describe the role of nanotechnology in EMI shielding?
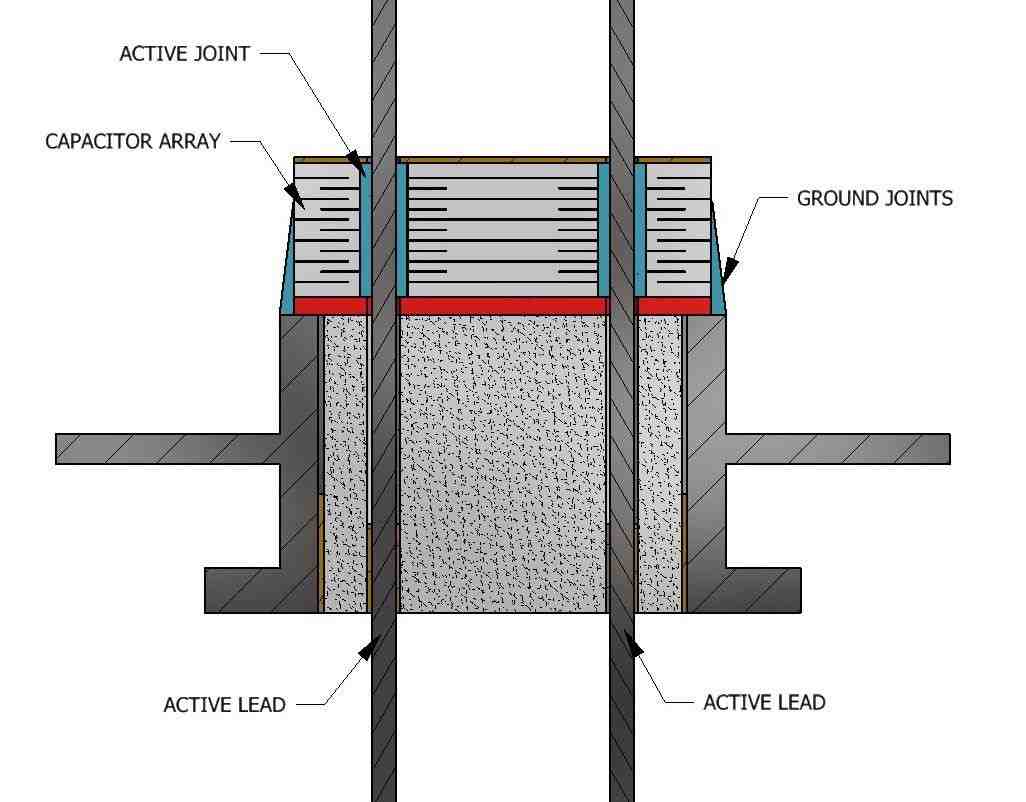
Interconnections can be an important carrier of RF EMI signals. A major “RF” violator would be any signal that falls in one of the assigned radio bands as defined by governments around the world. Conductors, carrying a high-frequency RF signal, will generate harmonic electric and magnetic fields that can cause a replica of the signal to be received by a neighboring interconnect.
Switching harmonics, generated by switching or through power converters, will also generate a high radiated and conducted EMI appearing at the switching power converter outputs.
In addition, RF EMI can arise from switching harmonics or even switching states of digital signals. This type of noise may appear as a capacitively or inductively induced pulse on nearby connections and cables rather than random noise.
Finally, RF EMI from external sources can come from an electrostatic discharge (ESD), which can conduct a broadband pulse into your system design or even be injected as conducted EMI through a power input.
Electromagnetic Shielding
Electromagnetic shielding will prevent an electromagnetic field from entering an RF design by blocking the field with various barriers made of conductive or magnetic materials. Shielding is usually applied to enclosures to isolate electrical/electronic devices from their noisy environment.
In addition, shielding is applied to cables to isolate wires from the environment through which the cable passes. Electromagnetic shielding, which blocks radio frequency electromagnetic radiation, is known as RF shielding. Shielding can also reduce the coupling of radio waves, electromagnetic fields and electrostatic fields to a designer’s circuit.
A conductive housing used to block electrostatic fields is called a Faraday cage. The amount of EMI reduction strongly depends on the material used, the thickness, the size of the shielded volume and the frequency of the regions of interest. Other factors include the size, shape and orientation of any openings in the shield to an incident electromagnetic field.
Electrostatic Shielding
The sensitivity/susceptibility to static electricity (known as electrostatic discharge or ESD) in high speed, high power density electronic circuits is much higher compared to low speed, low power density circuits.
Static electricity, external to your design, can cause catastrophic failures in your circuit design. To prevent a high-level external electric field from damaging your design, the use of electrostatic shielding will provide a barrier to effectively insulate your circuit.
Electrostatic shields can contain small gaps that are allowed in electrostatic shields since the electric field in the cavity is relatively small for such gaps. This type of shield also reduces the expenditure on ventilation. Such openings are also sometimes used for cable or wire harnesses, as well as access points to the internal circuitry.
EMI Filtering for RF Designs

Passive filtering is a method that will reduce conducted emissions from an electronic circuit by using inductors and capacitors to create an impedance mismatch in the EMI current path. Active filtering can also be used to detect the voltage on the input bus and produce a reverse phase current that directly cancels the EMI current generated by a switching stage.
The figure shows a simplified passive and active filter circuit where iN is the current source and ZN is the impedance of the Norton equivalent circuit for differential mode noise of a dc-dc regulator.
The filter design shown in the picture can be used in automotive applications. The active filter uses voltage sensing and current injection, which enables a low EMI signature and leads to a smaller footprint and volume, as well as improved solution costs. The integration of an active EMI filter (AEF) circuit, which uses a synchronous buck controller, helps solve the trade-offs between low EMI and high power density in dc-dc regulator applications.
Summary

RF shielding is the practice of blocking electromagnetic RF signals, EMI, which can cause radio frequency interference (RFI). RFI can severely reduce the performance of electronic circuits or even disable proper circuit functions.
RF shielding is a means of protecting a circuit designer’s devices and equipment from the harmful effects of RFI. This can be achieved by placing barriers around potential sources and victims of electromagnetic fields. Filtering of RFI is accomplished within the electronic system through circuitry that allows only desired signals to pass and reject unwanted RFI signals.
Read more articles in the TechXchange: Diving into EMI, EMC and noise
References
1. “Ten Tips for Successful Designing with Automotive EMC/EMI Requirements,” Texas Instruments.
2. “How to Reduce EMI and Reduce Power Supply Size with Integrated Active EMI Filter”, Texas Instruments.
Does foil block EMI?
Aluminium. Due to its strength-to-weight ratio and high conductivity, aluminum can work well as an EMI shielding material.
Is Stainless Steel Good for EMI? For the shielding, materials must have a high conductivity. Such as steel, copper, aluminum, stainless steel, etc., are the most commonly used materials for EMI shielding.
What absorbs EMI?
RFI and EMI shielding materials are designed to absorb, reflect or divert electronic noise from or around sensitive devices and circuits. Common shielding materials include aluminum, copper, tin, epoxy and ferrite powders, gold cloth, nickel, nitrile, and forms of polyester.
What is EMI shielding material?
Introduction. Shielding by electromagnetic interference (EMI) refers to the shielding of radio wave or microwave radiation so that the radiation cannot essentially penetrate through the shielding, which serves as a radiation barrier. EMI shielding should be distinguished from magnetic shielding.
How can I shield against EMI?
Today, EMI shielding materials include flexible metal screens, metal wires and metal foam. Coatings made from metallic inks are also applied to the inside of electronic housings to provide an EMI shielding solution.
What metal blocks EMF best?
Copper is the most reliable material of choice for shielding radio frequencies because of its ability to absorb both magnetic and radio waves. It is also very effective at damping magnetic and electrical waves.
Does steel protect against EMF?
Typical materials used for electromagnetic shielding are sheet metal, metal screen and metal foam. Common sheet metals for shielding include copper, brass, nickel, silver, steel, and tin.
Is aluminum foil a good RF shield?
At frequencies from 30 to 100 MHz, aluminum foil provides a shielding effectiveness of at least 85 dB. Unfortunately, aluminum foil is extremely unsuitable against low-frequency magnetic fields, where thick steel or highly permeable ferrite material provides more adequate shielding.
How can I shield against EMI?
Today, EMI shielding materials include flexible metal screens, metal wires and metal foam. Coatings made from metallic inks are also applied to the inside of electronic housings to provide an EMI shielding solution.
How can I protect against EMI?
Common techniques to minimize EMI include line filtering, power supply design, proper enclosure layout, and shielding. Electrical disturbances can be conducted through the power lines or transmitted through the air by capacitive, magnetic or electromagnetic radiation.
How is EMI shielding tested?
Shield effectiveness is measured by comparing the readings of the reference and the load devices. This method is effective for frequencies less than 500 megahertz. It involves using a sealed box with an opening. A shielding unit is inserted through the opening of the box.
Can copper block magnetic fields?
Electromagnetic shielding is the process of lowering the electromagnetic field in an area by barricading it with conductive or magnetic material. Copper is used for radio frequency (RF) shielding because it absorbs radio and other electromagnetic waves.
What material can block a magnetic field? MuMetal® is the most commonly used alloy for magnetic shielding purposes. The composition of 80% nickel, 4.5% molybdenum and balance iron gives it very permeable properties. This tells us that the material has a high magnetic sensitivity to an applied magnetic field; it easily accepts the flow of magnetic field.
How do you disrupt a magnetic field?
If you want to block magnetic “force”, it is best to reroute magnetic field lines (lines of magnetic flux) around the object sensitive to those lines. Do this by shielding the object in a material with a much higher magnetic permeability from the surrounding materials.
How do you stop a magnetic field?
The simple answer is that it is not possible to completely ‘block’ a magnetic field. The essence of a magnet, as defined by nature, is that magnetic field lines must end at the opposite pole and therefore there is no way to stop them. Our own Earth’s magnetic field is a perfect example of this.
Can anything block a magnetic field?
The short answer is no, there is no shield or substance that will effectively block magnetic fields as such. However, you can reroute the magnetic field lines, which some people call magnetic shielding.
Is it possible to block a magnetic field?
Magnetic fields cannot be blocked, only redirected. The only materials that divert magnetic fields are those that are ferromagnetic (attracted to magnets), such as iron, steel (which contains iron), cobalt, and nickel. The degree of diversion is proportional to the permeability or density of the material.
Can you block the Earth’s magnetic field?
The simple answer is that it is not possible to completely ‘block’ a magnetic field. The essence of a magnet, as defined by nature, is that magnetic field lines must end at the opposite pole and therefore there is no way to stop them. Our own Earth’s magnetic field is a perfect example of this.
How can we stop magnetic fields?
February 2004. The short answer is no, there is no shield or substance that will effectively block magnetic fields as such. However, you can reroute the magnetic field lines, which some people call magnetic shielding.
How do you use EMI shielding tape?
How does EMI shielding tape work? When signals reach your device, the screen absorbs them, creating a current in the body. An earth connection or a virtual ground plane then absorbs this current. The EMI shield absorbs transmitted signals before they reach sensitive circuitry on your device, keeping your protected signal clean.
What is EMI shielding material?
Introduction. Shielding by electromagnetic interference (EMI) refers to the shielding of radio wave or microwave radiation so that the radiation cannot essentially penetrate through the shielding, which serves as a radiation barrier. EMI shielding should be distinguished from magnetic shielding.
What is the purpose of EMI RFI shielding?
EMI shielding and RFI shielding reduce susceptibility to electronic interference by blocking unwanted external electromagnetic waves or preventing internal electromagnetic waves from emitting and interfering with other circuits or devices.
What is shielding material?
Materials used Common sheet metals for shielding include copper, brass, nickel, silver, steel, and tin. Shield effectiveness, ie how well a shield reflects or absorbs/suppresses electromagnetic radiation, is affected by the physical properties of the metal.
How do you do EMI shielding?
This is achieved by using a metal screen to absorb the electromagnetic interference transmitted through the air. The shield effect is based on a principle used in a Faraday cage: the metal shield completely surrounds the sensitive electronics or the transmitting electronics.
How is EMI shielding tested?
Shield effectiveness is measured by comparing the readings of the reference and the load devices. This method is effective for frequencies less than 500 megahertz. It involves using a sealed box with an opening. A shielding unit is inserted through the opening of the box.
How can I protect against EMI?
Common techniques to minimize EMI include line filtering, power supply design, proper enclosure layout, and shielding. Electrical disturbances can be conducted through the power lines or transmitted through the air by capacitive, magnetic or electromagnetic radiation.
Does EMI shielding need to be grounded?
* A ground is not necessary for EMI control (although it may be necessary for safety). What is needed is a low impedance current return path, usually a conductive face or shield.
What is the purpose of EMI RFI shielding?
EMI shielding and RFI shielding reduce susceptibility to electronic interference by blocking unwanted external electromagnetic waves or preventing internal electromagnetic waves from emitting and interfering with other circuits or devices.
How can I protect my EMI from wire?
Use shielded twisted pair cable to carry instrumentation signals. Twisting the wires equalizes the effect of EMI on both wires, greatly reducing the error due to EMI. Surrounding the instrument wires with a shield protects them from EMI and provides a path for EMI-generated current to flow to ground.
Is shielding an effect?
The shielding effect describes the balance between the attractive force of the protons on valence electrons and the repulsive forces of internal electrons. The shielding effect explains why valence shell electrons are more easily removed from the atom. The effect also explains the atom size.
What is an example of a shielding effect? The shielding effect is when the electron and nucleus in an atom have a decrease in attraction causing the nuclear charge to change. An example of a shielding effect is in nuclear fission when electrons furthest from the center of the atom are pulled away.
Is shielding effect same as screening effect?
The shielding effect is also known as the shielding effect. The phenomenon occurs when the nucleus decreases its attraction to the valence electrons due to the presence of electrons in the inner shell. This is known as a screening effect.
Why shielding effect is called screening effect?
When the number of inner electrons is greater, they shield the outer electron from the nucleus, so that the outer electron becomes free of any nuclear attraction. This is called the shielding or shielding effect.
What is effective shielding effect?
The effective nuclear charge (often symbolized as Zeff or Z*) is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom. The term “effective” is used because the shielding effect of negatively charged electrons prevents higher orbital electrons from experiencing the full nuclear charge.
What is a shielding effect in chemistry?
In chemistry, the shielding effect is a state in which an electron shields itself from the nucleus. The electrons present in the atom are not affected by the nucleus. It is also known as the screening effect.
What does shielding effect mean in chemistry?
The shielding effect can be defined as a reduction in the effective nuclear charge on the electron cloud, due to a difference in the attractive forces on the electrons in the atom. It is a special case of electric field screening.
What is the shielding effect for dummies?
The shielding effect is the decrease in the attractive force between an electron and the nucleus caused by the other electrons in the atom. The electrons between an outermost electron and the nucleus cancel some of its charge. upload.wikimedia.org. Thus, the nucleus cannot attract the outermost electrons with its full charge.
What is EMI shielding describe the role of nanotechnology in EMI shielding?
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials prevent the transmission of electromagnetic (EM) radiation by reflection and/or absorption or by suppression. Emerging nanomaterials can be used effectively for EMI shielding.
What is EMI Shielding? EMI shielding in electronic devices and equipment is the use of manufacturing techniques and materials to protect signals from interference from external electromagnetic signals and to prevent generated signals from interfering with surrounding components.
What are shielding techniques?
EMI shielding is a technique to create a barrier that prevents leakage of strong electromagnetic fields that can disrupt sensitive devices and signals. They can be installed to isolate the source of the electromagnetic field or as a housing of the device to be protected.
What is shielding and why it is used?
EM shielding is performed for several reasons. Its most common purpose is to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) from affecting sensitive electronics. Metal mesh shields are often used to protect one part from attacking another part in a given device.
What is shielding in electrical?
Imposing a metallic or composite barrier between one or more sources of electrical noise and their victims for the purpose of reducing or eliminating electrical interference.
What do u mean by shielding?
Definition of shielding: Something that shields or protects Options include a night vision camera, shielding under the body to help protect against landmines and bombs, as well as radiation detection equipment.”
Why is RF shielding important?
RF shielding and magnetic shielding RF shielding is specific for blocking radio frequency electromagnetic radiation. Shields that are effective at blocking RF waves, as well as other types of waves, are sometimes called EMI/RFI or EMF shields.
What does an RF shield do?
Radio frequency (RF) shielding is a solution used for blocking radio frequency interference. It involves the construction of an enclosure to reduce the electrical and magnetic transmissions from one room to another.
Why is EMI important?
Whether small or large electronic equipment, exposure to a wide range of interference or frequencies cannot be avoided. Therefore, shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) is crucial to ensure that there is no infiltration into the devices.


