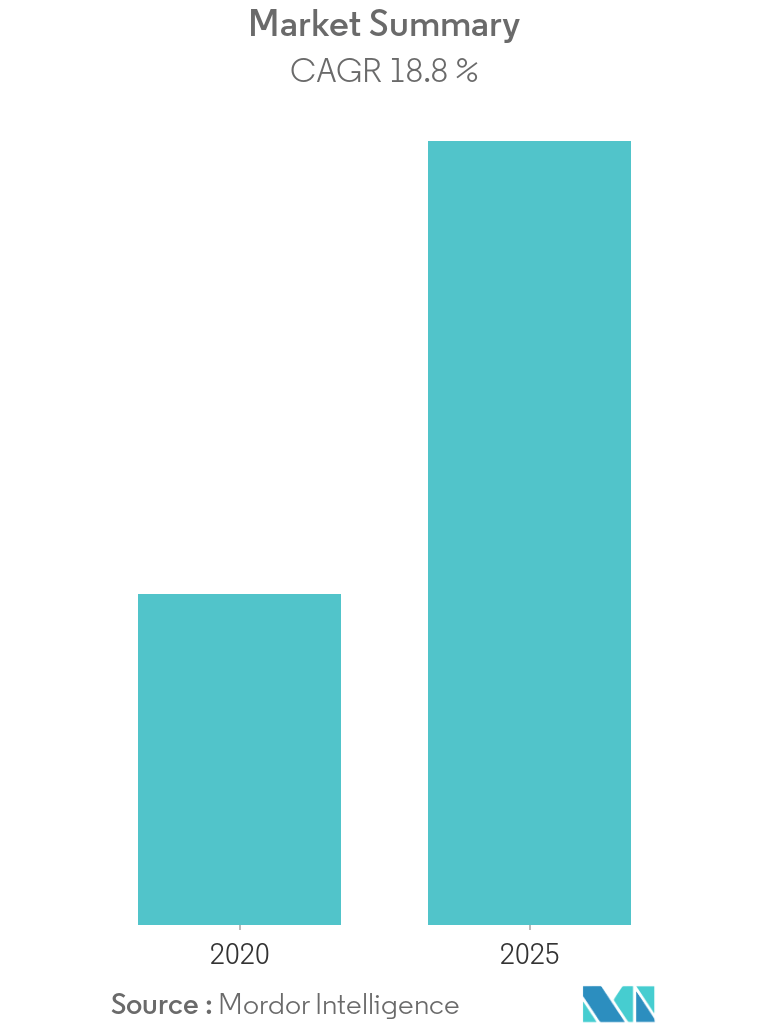A new MarketQuest.biz report, titled Global Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Market from 2022 to 2028, provides information and measurements on market design and size. The exam is likely to provide market knowledge and key experiences that will help leaders decide on educated speculative choices and distinguish upcoming holes and openings in development. The motivation behind this review is to revise market patterns and developments from top to bottom, so that appropriate methodologies can be applied to outperform the global RFID market.
The scope of the task, creation, fabrication of respect, misfortune / benefit, offer / request, and import / shipment are shown in full. Statistical research then, at that time, evaluates business development designs around the world of radio frequency identification (RFID). It additionally contains data on important associations. The practicality test, SWOT investigation and profit from speculation investigation are fully remembered for this review.
DOWNLOAD FREE SAMPLE REPORT: https://www.marketquest.biz/sample-request/96294
The development planning measure requires departmental investigation as it allows suppliers to continuously monitor requirements, allowing them to prepare and adjust market interests and offers. The survey adopts an expansive strategy of detecting neglected market pathways and opportunities. In light of substantive research and ancillary top-to-bottom review, the report is framed on the basis of current patterns, evaluation of research, potential and past interests and supply, monetary situation, impact of COVID-19 and different perspectives. Industry-trained experts and our in-house space experts embrace essential research.
Market overview by applications:
The report additionally contains the worldview of key districts, in particular:
The main players in the market are:
ACCESS THE COMPLETE REPORT: https://www.marketquest.biz/report/96294/global-radio-frequency-identification-rfid-market-2022-by-company-regions-type-and-application-forecast-to-2028
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) on a global scale Highlights from the market report:
This report can be tailored to customer requirements. Contact our sales team (sales@marketquest.biz), who will make sure you get a report that fits your needs. You can also contact our executives at 1-201-465-4211 to share your research requests.
Contact us Mark Stone Head of Business Development Phone: 1-201-465-4211 Email: sales@marketquest.biz
How many types of RFID are there?
Contents
Each RFID device operates at a specific frequency for data communication. Depending on this frequency, RFID technology can be divided into three categories – low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF) and ultra high frequency (UHF).
How much RFID is there? 1 will need two separate radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, according to the Toll Regulatory Board (TRB).
What are the different types of RFID?
Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive (powerless) or semi-passive (battery powered).
- Low frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. …
- High frequency (HF) RFID tags: 3 to 30 MHz. …
- Ultra high frequency (UHF) RFID tags: 300 MHz to 3GHz. …
- Active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.
How do I know what type of RFID I have?
You can check the uid number printed on the card (the number related to the chip) if it starts with three or four zeros and its rfid type.
Are all RFID cards the same?
Not all RFID cards are the same. There are two types of cards: RFID contactless cards with 125KHz and 13.56Mhz frequency chips. The first type of chip is called Low Frequency (LF), the second – High Frequency (HF).
Are all RFID cards the same?
Not all RFID cards are the same. There are two types of cards: RFID contactless cards with 125KHz and 13.56Mhz frequency chips. The first type of chip is called Low Frequency (LF), the second – High Frequency (HF).
Can any RFID reader read any RFID tag?
RFID tag technology In most cases, each type of passive RFID tag (LF, HF or UHF) can only be read by the SAME type of passive RFID reader. For example, usually an LF reader will only be able to read an LF tag; will not be able to read the HF or UHF tag.
How do I know what kind of RFID card I have?
You can check the uid number printed on the card (the number related to the chip) if it starts with three or four zeros and its rfid type.
Who uses Zebra Technologies?
| Company name | Website | State |
|---|---|---|
| Lockheed Martin | lockheedmartin.com | US |
| PerkinElmer | perkinelmer.com | US |
| Starkey Hearing Technologies | starkey.com | US |
| Tiffany & amp; Co. | tiffany.com | US |
What is Zebra MotionWorks? Zebra MotionWorks® Enterprise, the cornerstone of the industry’s widest field-proven RFID portfolio, is an innovative platform that enables transportation and logistics vendors, manufacturing companies and healthcare organizations to turn enterprise property locations into practical business insights.
What does Zebra technology do?
Zebra Technologies Corporation is an American mobile computing company specializing in technology used for real-time detection, analysis and operation. The company manufactures and sells labeling, tracking and computer printing technologies.
Where is Zebra headquarters?
What is Zebra program?
Zebra software makes it easy to create and print cards, manage and set up network printers, and easily integrate card printing into new and existing applications. Whether you are a small business or a larger business, Zebra has the right software to meet your needs and manage your card printers.
What is Zebra application?
Zebra TechnologiesProductivity. Everyone. Mobile printing is easy! Zebra Utilities allows you to print barcode labels and invoices directly to a Zebra Technologies printer via Bluetooth or WLAN.
What is Zebra tool?
The body. Original Zebra thermal printing material. Supplies Network offers Zebra supplies, a leading brand in the industrial thermal printing market. These sought-after products are critical to supporting operational efficiency and maintaining compliance in many industries.
Is RFID a part of IoT?
By connecting an RFID reader to an Internet terminal, readers can globally, automatically, and real-time identify, track, and monitor tagged objects, if needed. This is the so-called Internet of Things (IoT). RFID is often considered a prerequisite for IoT.
What role does RFID play in the Internet of Things environment? In other words, the function of RFID technology in IoT is to connect objects to a network and create and send data.
Does RFID use Internet?
Passive RFID readers have a power source – usually AC power, Ethernet power (PoE) or battery. They also have data transfer capabilities such as Ethernet, WiFi or cellular network, and can be assigned an IP address. So, according to the previous definition, passive RFID readers can join “Internet devices”.
Can RFID be connected to Internet?
The RFID reader connects to the server by running some intermediate software that filters the collected data and stores it in a database. You could then make the information in the database available online, just as you would with any other online database.
What technology is used in RFID?
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that involves the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency part of the electromagnetic spectrum for the unique identification of an object, animal or person.
What is the difference between IoT and RFID?
RFID is a type of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. IoT is a network of devices with sensors and actuators that collect and send data over the Internet.
Quels sont les IoT ?
L’IoT reinvente l’automobile and rents possible connected vehicles. Thanks to IoT, the owners of cars can control the distance; ils peuvent, par exemple, préchauffer la voiture avant d’y monter, ou appeler une voiture à distance par telephone.
Qu’est-ce qu’un capteur IoT ?
Captain IoT: the support of intelligent objects Conclusion: a collector of data from a platform via a platform, for a simple coyote. Are there more appeals to the IoT? It is an agit of a technology plus or less complex that measures the data and detects changes in the environment.
What is RFID in IoT?
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that involves the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency part of the electromagnetic spectrum for the unique identification of an object, animal or person.
Which layer in IoT uses RFID?
(i) The transport layer transmits sensor data from the perception layer to the processing layer and vice versa via networks such as wireless, 3G, LAN, Bluetooth, RFID and NFC. (ii) The process layer is also known as the interlayer layer.
How does RFID work in IoT?
Radio frequency identification â € “or RFID â €“ is used to automatically identify an object and capture data about that object that is stored in a small microchip and attached to the object. The RFID tag has a built-in antenna that communicates with a scanning device that remotely reads data.
What are two types of RFID?

RFID systems can be broken down according to the frequency range within which they operate: low frequencies, high frequencies and ultra high frequencies. There are also two broad categories of systems – passive and active RFID. In the sections below, we will explore the frequencies and types of RFID systems.
Can RFID chips be hacked? RFID hackers have shown how easy it is to access information within RFID chips. As some chips can be rewritten, hackers can even delete or replace RFID information with their own data. It’s not too hard for a hacker to make his own RFID scanner if he wants to.
What is a 125kHz RFID?
RFID is useful for detecting and identifying tagged people and objects for access control, automation and a variety of different applications. This basic RFID tag operates in the 125 kHz RF band and comes with a unique 40-bit ID. Cannot be reprogrammed.
What uses 125KHz RFID?
Application of 125KHz RFID TAGS The most common uses of these tags range from anti-counterfeiting, logistics, access control, ticketing to industrial transponder, manufacturing, industrial automation, high hands-free security and production automation.
What is the difference between 125KHz and 13.56 MHz?
This will affect 125KHz and 13.56MHz RFID signals. In this environment, the higher frequency(13.56MHzï¼ ‰ still maintains an acceptable working distance of 3-5cm, better than 125KHz (left only 1-2cm). System expandability-13.56MHz RFID based on 8Kbit card capacity. This card can hold much more data than a 125KHz card.
What are the three types of RFID?
Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive (powerless) or semi-passive (battery powered).
- Low frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. …
- High frequency (HF) RFID tags: 3 to 30 MHz. …
- Ultra high frequency (UHF) RFID tags: 300 MHz to 3GHz. …
- Active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.
What is UHF RFID used for?
Passive UHF RFID applications Passive UHF RFID systems are used in hundreds of different applications such as tool tracking, IT asset tracking, race time measurement and laundry management. New applications for these tags are often discovered primarily due to the large range of tag readings and low cost.
Can RFID chips be cloned?
In particular, RFID tags are prone to basic security attacks of cloning and counterfeiting. Successful cloning of RFID tags in many commercial applications can lead to many serious problems such as financial losses, brand damage, security and public health.
Can RFID chips be encrypted?
For security, RFID signals can be encrypted. Chips that will enter U.S. passports, for example, are likely to be coded to make it harder for unauthorized readers to retrieve information on board (which will include a person’s name, age, nationality, and photograph).
How do you stop RFID cloning?
The easiest way to protect yourself is to use a wallet or RFID blocking cover. This simply works by blocking the signal from the card. If there is no signal, the jammers cannot retrieve the unique information on the card and it cannot be cloned.
What is RFID tag clothing?
RFID tagging helps track goods from production to storage and allows any damage to be scanned at each checkpoint. Better inventory control: RFID tagging helps the retailer locate clothing inventory.
How do RFID tags for clothing work? Using RFID tags saves time, effort and money. This process automatically identifies objects, collects data about them and enters that data directly into computer systems with little or no human intervention. This reduces production, shipping, inventory review and sales.
Some of the main areas of today’s use of RFID tags are: identification of animals (pets, livestock, laboratory animals) Contactless access control systems. Contactless payments.
This information can include anything from name, condition, quantity and location. Through the constantly pulsating radio waves of the RFID tag, the RFID reader is able to capture the stored data. Eventually they are collected in a sophisticated asset tracking system where data can be tracked and acted upon.
An active RFID system can be implemented quickly, allowing you to track people in locations where you may have needed expensive GPS devices in the past. With Active RFID, you can track people anywhere while moving freely without the need for portal technology.
What does RFID stand for in clothing?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification and is a method used to track goods via wireless signals, in order to transfer data between microchips. Chips are usually inserted into labels or cards that contain electronically stored information and transmit a radio signal.
Yes. Many companies produce RFID tags coated with protective plastic. These markings are designed for use in laundry and uniform rental. The labels used are usually 13.56 MHz labels, which have a reading range of less than 3 feet (1 meter).
What is RFID short for?
Description. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) refers to a wireless system that consists of two components: a tag and a reader. A reader is a device that has one or more antennas that emit radio waves and receive signals back from the RFID tag.
Who is the CEO of Zebra?
Where is Anders Gustafsson from? Anders Karl Gustaf Gustafsson (born April 7, 1979 in Jönköping) is a Swedish sprint canoeist who has been competing since the mid-2000s.
How old is Anders Gustafsson?
Anders Gustafsson, 60, is a CEO and board member of Zebra Technologies Corporation, a global leader in enterprise edge innovation, specialty printer design and marketing, mobile computing, data collection, radio frequency product identification and real-time …
Who owns Zebra printers?
Zebra printers got their name from being produced by Zebra Industries. Since its founding in 1991, this public company has become a global leader in the industry of barcoding and RFID technology.
Why is it called a Zebra printer?
Zebra printers got their name from being produced by Zebra Industries. Since its founding in 1991, this public company has become a global leader in the industry of barcoding and RFID technology. It focuses on providing high-speed electromagnetic products that are unsurpassed in quality and efficiency.
What is Zebra Technologies Corp?
Zebra Technologies Corporation designs and manufactures business mobile PCs, advanced data capture devices such as laser, 2D and RFID scanners and readers, and special bar code printers and personal identification.