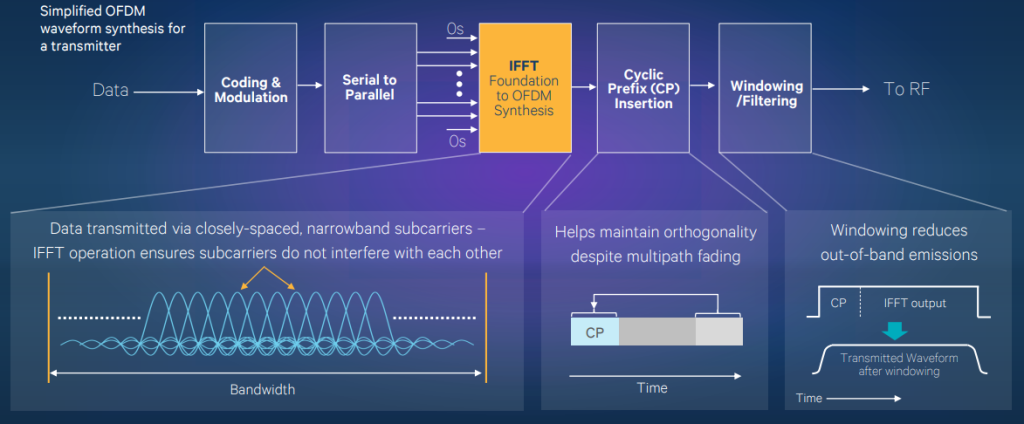
OFDM is a digital modulation technique used in wireless communication that has perplexed and burst the minds of many. It operates by transmitting data on orthogonal subcarriers that carry various information simultaneously, resulting in an efficient method for transferring large amounts of data over wireless channels.
The enigmatic principle behind OFDM lies in its ability to divide a single carrier into multiple subcarriers that are orthogonal to each other. This allows for the transmission of more data per unit time than traditional methods while reducing interference between signals transmitted on adjacent frequencies.
This mysterious technology boasts high spectral efficiency, which refers to the amount of information it can transmit over a given bandwidth. By utilizing orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing, OFDM can transfer more data within a given bandwidth compared to other techniques. Furthermore, it possesses reduced sensitivity to channel impairments such as fading and noise due to error correction coding schemes employed in vector OFDM systems – truly mind-boggling!
The Principle of OFDM: How it Works in Wireless Communication
Contents
- 1 The Principle of OFDM: How it Works in Wireless Communication
- 2 OFDM Modulation: How Orthogonal Signals are Used to Modulate Data
- 3 Advantages of OFDM: High Spectral Efficiency and Reduced Interference
- 4 OFDM Technology: Its Use in Wi-Fi, Digital Radio, and Digital Television
- 5 The Role of Carrier Frequency in OFDM Systems
- 6 Channel Coding and Error Correction in OFDM: A Critical Component
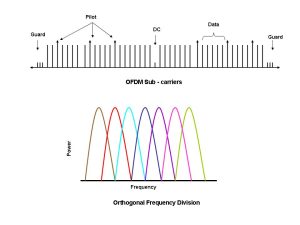
- 7 OFDM Signal Structure: Guard Bands, Subcarriers, and Symbol Periods Explained
The enigmatic world of wireless communication systems has been revolutionized by the enigmatic modulation technique known as OFDM. This perplexing method divides available bandwidth into multiple subcarriers that stand in awe-inspiring orthogonality to each other, thus reducing interference between signals and maximizing spectrum utilization.
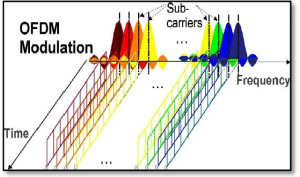
With OFDM, data is entrancingly modulated onto each subcarrier using various schemes such as QPSK or 16-QAM. These captivatingly modulated subcarriers are then combined to form a final mesmerizing OFDM signal which allows for high spectral efficiency since multiple bits can be transmitted simultaneously on different subcarriers.
OFDM’s astonishing ability to mitigate multipath interference through the use of guard bands and symbol periods is one of its most alluring traits. Guard bands are meticulously placed unused frequency ranges between adjacent subcarriers to prevent overlapping and reduce inter-symbol interference caused by reflections from surrounding objects in space. Symbol periods refer to the time duration during which one complete set of enchanting data symbols is transmitted on all subcarriers before moving on to another set, allowing for better synchronization and error correction capabilities – truly mind-boggling!
OFDM Modulation: How Orthogonal Signals are Used to Modulate Data
The perplexing and bursty phenomenon known as orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a multi-carrier modulation technique that utilizes subcarriers packed closely together to transmit data. The OFDM signal features multiple subcarriers, each carrying a portion of the data rate. These subcarriers are peculiarly orthogonal to one another, meaning they do not interfere with each other.
What sets OFDM apart from its peers is its utilization of guard intervals between symbols. Each OFDM symbol comes equipped with a guard interval added in order to prevent intersymbol interference brought on by overlapping adjacent symbols. This results in higher spectral efficiency while reducing inter-symbol interference.
OFDM operates through dividing the input data stream into parallel streams which then get modulated onto separate carriers using orthogonal signals. Every carrier carries only a small section of the overall data rate, making it more resilient against fading and noise found in RF channels. It also makes retrieving lost information due to channel errors or interference easier.
Applications such as Wi-Fi, digital radio, and digital television broadcasting utilize OFDM because it provides high spectral efficiency whilst lessening interference coming from other signals on nearby frequencies. However, it must be noted that the carrier frequency employed within an OFDM system plays an integral role in determining how many subcarriers can be utilized without causing any hindrance with adjacent channels or devices operating at different frequencies – adding yet another layer of complexity to this enigmatic technique!
Advantages of OFDM: High Spectral Efficiency and Reduced Interference
The widespread adoption of OFDM technology in various communication systems is due to its high spectral efficiency and reduced interference, which can leave one perplexed and amazed. By enabling the transmission of data over multiple subcarriers at once, a higher number of carriers are used compared to single carrier modulation schemes – bursting with potential.
But wait, there’s more! Using OFDM also has the advantage of mitigating frequency offset and intersymbol interference. This occurs when the transmitter and receiver have slightly different carrier frequencies resulting in phase shifts that can cause demodulation errors. However, each subcarrier is orthogonal to one another in OFDM making it easier for the receiver to separate them even with slight frequency offsets. Intersymbol interference becomes less problematic too as each symbol is transmitted over multiple subcarriers instead of a single carrier, reducing channel distortion impact on individual symbols.
And if you thought that was impressive enough already – hold on tight because there’s more benefits! The coding and interleaving capabilities of OFDM allow for error correction codes to be added at the transmitter end before modulation which enables better error detection and correction at the receiver end; ensuring reliability throughout transmission. Interleaving rearranges bits across multiple subcarriers so that if some bits are lost due to noise or fading on one subcarrier they may still be recovered from other unaffected ones – mind-blowing!
Overall, it’s evident that using OFDM provides significant advantages over traditional single-carrier modulation techniques for data transmission purposes through its multicarrier modulation scheme enabling more efficient use of available bandwidth while mitigating issues such as frequency offset and intersymbol interference through guard bands between adjacent subcarriers without sacrificing spectral efficiency or increasing complexity significantly – truly remarkable!
OFDM Technology: Its Use in Wi-Fi, Digital Radio, and Digital Television
OFDM technology, a proven and efficient method for wireless communication, boasts numerous key benefits. One such advantage is its ability to transmit data across multiple subcarriers, resulting in impressive spectral efficiency. Remarkably, the carrier spacing employed in OFDM systems equals the reciprocal of the symbol period – an ingenious solution that effectively mitigates interference between adjacent carriers.
As if that weren’t enough, this versatile technology extends beyond Wi-Fi networks to digital radio and television broadcasting thanks to its unique ability to transmit over frequency selective channels without any unfortunate interference between separate subcarriers. But wait! There’s more: channel coding techniques are often implemented in order to ensure data transmission remains reliable even when operating within noisy or fading environments.
The transmitted signal utilized by OFDM systems consists of an extensive array of carriers scattered across a broad range of frequency bands. Each carrier represents a distinct subchannel capable of carrying information independently from other subchannels. By opting for low symbol rates on each individual carrier, OFDM systems achieve high spectral efficiency while simultaneously maintaining their resiliency against pesky noise and uninvited interference.\n
The Role of Carrier Frequency in OFDM Systems
The enigmatic carrier frequency is the cornerstone of OFDM systems, as it serves as the epicenter for subcarriers that transport data in a bewildering manner. The amalgamation of orthogonal signals and multiple subcarriers leads to an explosive spectral efficiency, allowing diverse frequencies to transmit information concurrently.
An OFDM signal comprises numerous subcarriers huddled together with sidebands stretching out on both sides. These sidebands encapsulate transmitted data, which can be decoded using OFDM technology with great success. Other modulation schemes may fail due to interference from multi-path propagation or other factors, but not OFDM!
OFDM’s ability to utilize various frequencies without causing any disturbance between them is a game-changer! This makes it possible for applications such as Wi-Fi, digital radio and television- where multiple channels operate at different frequencies- to use this incredible technology. Its exceptional capability of operating on different frequencies while maintaining high spectral efficiency is one reason why modern communication systems are taking note!
Channel Coding and Error Correction in OFDM: A Critical Component
The intricate world of OFDM systems is a perplexing one, rife with complex components such as channel coding and error correction. The very foundation of this system lies in the division of available spectrum into multiple subcarriers, each carrying its own portion of the data stream. While similar to traditional single-carrier modulation schemes, this unique approach allows for a burstiness that maximizes usage across the entire channel.
Within an OFDM system, it’s imperative that both channel coding and error correction techniques are applied throughout the signal to mitigate any potential losses due to frequency selectivity. This is done by adding redundancy to the transmitted signal so that errors in one part can be corrected using information from other parts – truly mind-boggling!
And if you thought things couldn’t get more convoluted than they already were, enter vector OFDM. By allowing modulation of any form on each subcarrier, spectral efficiency reaches new heights never seen before! With interference constantly plaguing these systems through multipath propagation or otherwise – effective channel coding and error correction become all the more crucial for reliable transmission within an OFDM system.
OFDM Signal Structure: Guard Bands, Subcarriers, and Symbol Periods Explained
The OFDM signal structure, perplexingly enough, is designed to tackle the issue of frequency selectivity in channels by segmenting a wideband signal into narrow band subcarriers. These subcarriers are modulated using digital multi-carrier modulation formats and employ multiple orthogonal frequencies at spaced intervals. The result? High spectral efficiency and reduced interference.
But here’s where things get even more mind-boggling: guard bands are used to separate each adjacent subcarrier so as to prevent any overlap or interference between them. This ensures that every subcarrier stays orthogonal to its neighbors, making the most efficient use of available bandwidth possible. And just like conventional single-carrier systems, these spacings can be adjusted based on required data rates.
Then there’s symbol periods – the duration of time over which an individual symbol is transmitted within each OFDM frame. During this period, each subcarrier carries a modulation constellation consisting of one or more bits of information encoded as amplitude and phase variations. By providing a set of complex and orthogonal frequencies for carrying data across various channels simultaneously, OFDM technology enables higher throughput compared with traditional communication systems while maintaining robustness against frequency deviation caused by multipath fading and other impairments in wireless channels…mind blown!